Plants are the living things that grow from tiny seeds or spores to mighty trees. They start their life as a weak creature that thrives on ground and water to grow. The starting point of their life is due to a process called germination. Germination allows the seeds – and also spores – to sprout and become a seedling (very young plant).
Plants are the living things that grow from tiny seeds or spores to mighty trees. They start their life as a weak creature that thrives on ground and water to grow. The starting point of their life is due to a process called germination. Germination allows the seeds – and also spores – to sprout and become a seedling (very young plant).
Parts of a Seed

Before discussing the process of germination, it is important to know about the parts of seeds. There are 3 main parts of the seed, which are:
- Seed Coat – The first things you can see on a seed is its coat – also called seed coat. It is usually a hard outer layer that protects the seed from damage. Also, many kinds of seeds have a soft seed coat that can easily be damaged by pressing them with hands.
- Embryo – The embryo is the actual part of a seed that grows from the cells that it contains to become a plant. It has 4 main parts, which are epicotyl, hypocotyl, radicle, and cotyledons.
- Endosperm – The endosperm is like a food storage for the seed. It usually surrounds the embryo of the seed, and it provides all the necessary food (starch and protein) until the seed germinates to a seedling.
Conditions for Germination
 Seeds depend on the environmental conditions for germination. Some seeds successfully germinate, while others don’t. Germination needs a right condition to sprout the seeds. The most important environmental conditions that need to be at the right level are water, temperature, oxygen, and light or darkness. Let’s discuss each of these environmental conditions.
Seeds depend on the environmental conditions for germination. Some seeds successfully germinate, while others don’t. Germination needs a right condition to sprout the seeds. The most important environmental conditions that need to be at the right level are water, temperature, oxygen, and light or darkness. Let’s discuss each of these environmental conditions.
- Water – The germination process highly depends on the amount of water present in the soil. Because seed coat is usually dry, it needs to be moistened by water to break its coating. Furthermore, when the water is absorbed in the seed, it activates the certain enzymes. These enzymes break down the stored food and convert it into useful chemicals that supply energy to the embryo.
- Temperature – Each kind of seed needs a different range of temperatures to germinate. Some seeds germinate in cold temperatures, while others require hot temperatures for germination. The seeds usually don’t germinate if the temperature is not favorable.
- Oxygen – seeds use oxygen during metabolism when germinating. Majority of the seeds are buried in the soil. Seed usually take oxygen from the spaces in the soil until they grow their leaves for photosynthesis. If a seed is buried at a great depth, then it is difficult for the seed to get oxygen.
- Light or darkness – It is not an important factor to consider. Because the majority of the seeds have no any effect of light or darkness. But, some seeds have the impact of light. The light or darkness usually trigger the germination process for these seeds.
Process of Germination
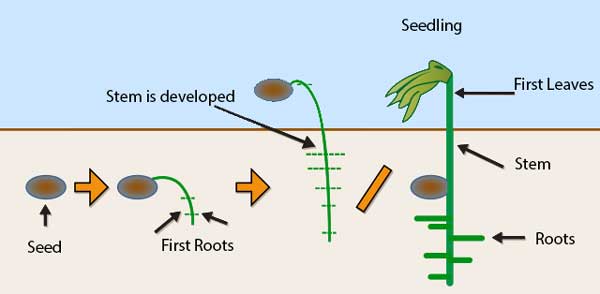
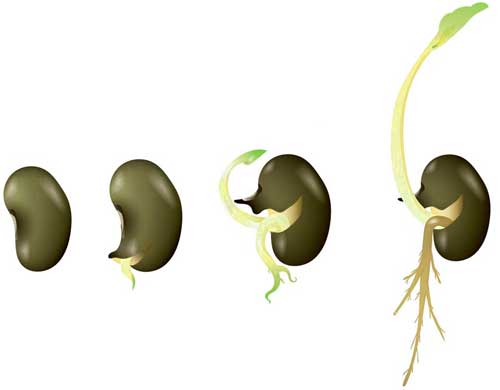 Germination of seed follows four main changes that are occurred in steps. These steps are imbibition, respiration, Mobilization of food reserves, and development of the embryo into a seedling. Let’s discuss each of these steps in detail.
Germination of seed follows four main changes that are occurred in steps. These steps are imbibition, respiration, Mobilization of food reserves, and development of the embryo into a seedling. Let’s discuss each of these steps in detail.
Imbibition
This is the first step that starts with the absorption of water – also called imbibition. As the seed absorbs the water through small pores in its seed coat, it rehydrates and swells. The swelling of the seeds forces the seed coat to break, which allows the radicle (first root) to come out and absorb nutrients from the soil.
Respiration
When water enters into seed, it starts the metabolic activities in the embryo. The oxygen is absorbed by the seed from the soil for generating energy. Oxygen provides the necessary energy to the seed until it grows leaves and starts
Mobilization of Food Reserves
During germination, metabolism takes place. The seed needs food for digestion. The food of the seed is usually stored in the endosperm. The food is mobilized from the endosperm to the embryo. The outer layer of the endosperm secretes the special enzymes that are used for digestion.
Development of Embryo into Seedling
 The transportation and digestion of food cause the cells of the embryo to develop and divide. The embryo grows until it forms into a seedling. The seedling has every necessary part to start photosynthesis and further grow into the mature plant.
The transportation and digestion of food cause the cells of the embryo to develop and divide. The embryo grows until it forms into a seedling. The seedling has every necessary part to start photosynthesis and further grow into the mature plant.
Rate of Germination
When the seeds are planted in an agricultural area or garden – not every seed in germinated. To measure how many seeds have been germinated from total seeds, it is called germination rate. Germination rate is usually in percentage, which describes how many seeds have been germinated in a given amount of time. For example, 100 seeds are planted in a garden and 65 seeds have been able to germinate. Then, the rate of germination will be 65%.
Facts
- The seeds of proteas have the unusual They start to germinate after they are exposed to smoke. This ability is definitely evolved in them for surviving in fire-catching forests.
- Coco-de-Mer is a seed that has a weight of around 30 kg. It is considered as largest seed on the earth.
- Not every plant grows from the seeds. Many plants grow from the spores of their parent plant. Spores are the remaining of a plant after it dies, or they may be the parts of a plant.