 Human and most of the animals are covered with a special organ, called skin. Skin is one of the important organs in our bodies which gives us protection and beauty. We are mostly recognized by our facial skin and other facial features. Let’s learn about this amazing organ in the human body and its functions.
Human and most of the animals are covered with a special organ, called skin. Skin is one of the important organs in our bodies which gives us protection and beauty. We are mostly recognized by our facial skin and other facial features. Let’s learn about this amazing organ in the human body and its functions.
What is Skin?
Skin is an organ in the human body that completely cover the body for keeping inside stuff safe from the outside world. It is the largest organ in our bodies which has many other functions besides being a protective layer.
Some parts of the human skin are covered with hairs, such as skin on the head. Whereas, the hairs on the body depends on person-to-person. Some people have more hairy skin than others which depends on their genetics.
Function of Skin
Human skin on the first sight may look simple to you, but it has many important functions to do. Let’s discuss some of the function of skin in detail.
- Protection – The skin is around 2 millimeters thick on most parts of the body. Protection is one of the fundamental function that the skin provides to the whole of our body. Skin prevents pathogens (bad microbes) and dust from entering in the body that may cause damage to our body otherwise.
- Sensation – Our skin is responsible for our sense of touch because it contains a large number of touch receptors. When you touch something, the receptor cells in the skin sends the messages to the brain to feel sensation. Touch sensors on our skin are able to sense coldness, warmth, pain, smoothness, and roughness. Every type of sensation has its own receptors that send signals to the brain when they are triggered. Some areas of the skin have densely populated touch sensors, such as lips, hands, and feet, to sense the small details on the objects.
- Body temperature control – After the protection and sensation, the next important job that the skin has to perform is to regulate the temperature of the body. When temperature of the body rises from normal values, the skin starts to sweat. Sweating cause the evaporation of water on the skin which results in cooling effect at the surface of the skin. Also, during the rise in temperature, the blood vessels in the skin become widen so that more blood can be cooled. But when the temperature of the body drops, the skin blood vessels become narrower to help the body in keeping the heat inside.
- Production of vitamin D – Some parts of the skin are able to synthesize vitamin D when sunlight hit them. Vitamin D is one of the essential vitamins that help calcium minerals in absorbing in our bodies. People having vitamin D deficiency can stay outdoor to synthesize vitamin D naturally.
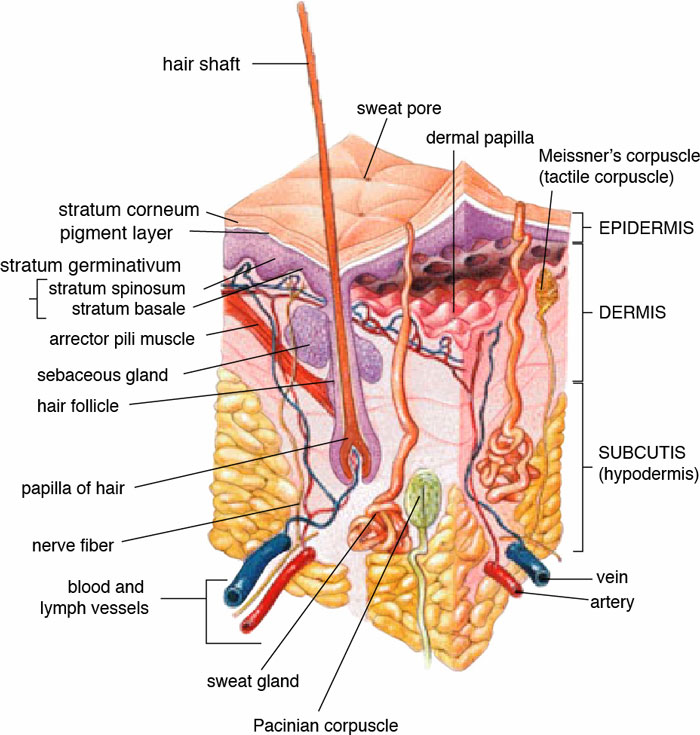
Layers of Skin
The skin of the human body has three main layers that serve their own function; epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis.
- Epidermis – It is the outer layers of skin whose very top surface has dead cells. This is the first layer of protection against pathogens and dust particles. Epidermis doesn’t have the supply of blood, and the cells have to survive on the oxygen from the atmosphere Also, the outermost cells in this layer are constantly replaced by new cells below them.
- Dermis – It is a thicker layer of the body which provide the body with a cushion against outside stress or strain. Dermis layers contain the nerve endings which are responsible for the sensation. Also, it contains hair follicles from which hairs grow, blood vessels, sweat glands, and some other things.
- Hypodermis – It is the 3rd layer which for various reasons not considered to be the part of our skin. The main purpose of this layer is to connect the underlying muscles and bones with the dermis layer, and supplying the dermis with blood vessels.
Facts
- An average sized person has around 2 square meters (21 square feet) of skin on its body, which contains around 300 million cells and weighs 9 pounds.
- If you connect all the blood vessels of the skin together, they will be around 11 miles (17.7 kilometers) long.
- Human skin contains a substance, called melanin, which gives it the color. If your body contains more melanin, your skin will be dark – like Africans.