Tag: light
-

Telescope
The telescope is an instrument that allows us to see the distant objects closer. We can view objects that are far beyond the range of our eyes. This instrument had opened the new door for us to study the space from the Earth and changed our understanding of the universe. […]
-

Light Bulb
Today electric lights have become the important and highly used appliance in our daily lives. We need it for lighting our houses, building and streets etc. Today we have handheld portable lights that can provide a backup time of more 12 hours. The technology that we use today may be […]
-

What is Electricity?
Electricity is the source of energy that is widely used by the peoples around the world. Today, life can’t be imagined without electricity. We use it all the time for lighting our houses, powering smartphones and computer etc. You have to just push a button and you have the electricity […]
-

How Rainbows work?
Rainbows are one of the beautiful masterpiece of nature. When they appear during rain they catch everybody’s attention by their beautiful seven bands of color in circular arc shape. Rainbows have inspired many artists and writer from centuries and many fairy tales were mainly inspired by them. Rainbow presents demonstration […]
-

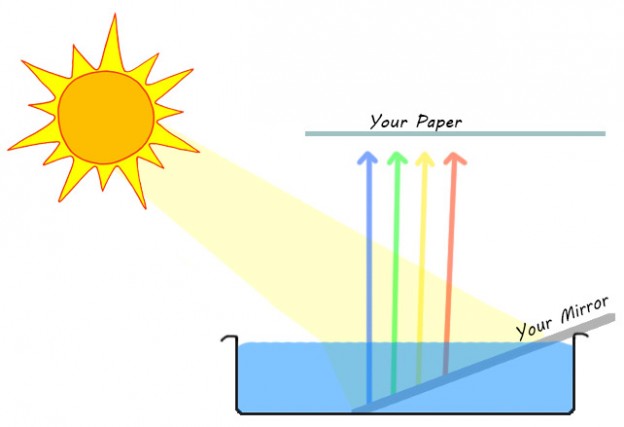
How to Make Rainbow on Paper
Want to get pleasure from natural rainbow colors? But you don’t want wait for rain. By knowing science you can. In this home experiment, we are going to make a rainbow on a paper by applying the same principle that a real rainbow follows. Except that, our homemade rainbow won’t […]