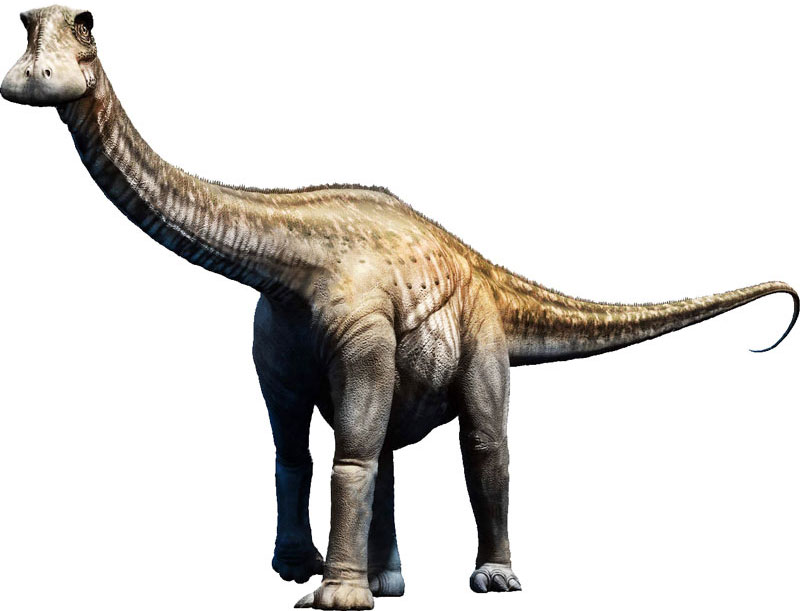
Nigersaurus are famous dinosaurs for having 500 slender teeth in their jaw. These dinosaurs have been recognized recently in the year 2000 and were named in the honor of country “Niger”. The word Nigersaurus has two parts; Niger (country name), and Saurus (reptile).
Nigersaurus are famous dinosaurs for having 500 slender teeth in their jaw. These dinosaurs have been recognized recently in the year 2000 and were named in the honor of country “Niger”. The word Nigersaurus has two parts; Niger (country name), and Saurus (reptile).
Nigersaurus lived around 100 million years ago in a period called the Cretaceous period that lasted from 145 to 66 million years ago. The genus of Nigersaurus contains only one species called ”Nigersaurus Taqueti”.
What Do They Look Like
 Nigersaurus is placed in the category of sauropods in which all the long-necked and long-tailed dinosaurs are placed. Nigersaurus was probably one of the smallest sauropods because its neck was short. An adult Nigersaurus weighed around 4 tons and its size was comparable to a modern elephant. The overall length of a typical Nigersaurus was around 9 meters (30 feet) including its tail. It had thick and stronger hind legs as compared to its front legs. Its neck was short and had 13 vertebrae in the cervical spine.
Nigersaurus is placed in the category of sauropods in which all the long-necked and long-tailed dinosaurs are placed. Nigersaurus was probably one of the smallest sauropods because its neck was short. An adult Nigersaurus weighed around 4 tons and its size was comparable to a modern elephant. The overall length of a typical Nigersaurus was around 9 meters (30 feet) including its tail. It had thick and stronger hind legs as compared to its front legs. Its neck was short and had 13 vertebrae in the cervical spine.
The skull of a Nigersaurus was made of thin bones and had many small openings and pores. These features provided them great flexibility in feeding on the ground. The muzzle of the Nigersaurus was wide and long which helped it in eating small ground-based vegetation. It had around 500 thin teeth in its jaw that were replaced with new teeth in 2 weeks. Its upper jaw teeth were larger than its lower jaw teeth. Moreover, Its jaw was much wider than the skull.
Habitat
 Nigersaurus preferred to live in areas having water lakes or streams nearby; the area is also called the riparian zone. Due to plentiful water, a riparian zone has a lot of low-lying vegetation. Riparian zones provide Nigersaurus with many types of vegetation. They thrived on the part of the Earth that we now call as Sahara Desert. However, During the Cretaceous period, the Sahara Desert was very green and hospitable. It was abundant in rivers, lakes, low-lying vegetation, and a variety of plants.
Nigersaurus preferred to live in areas having water lakes or streams nearby; the area is also called the riparian zone. Due to plentiful water, a riparian zone has a lot of low-lying vegetation. Riparian zones provide Nigersaurus with many types of vegetation. They thrived on the part of the Earth that we now call as Sahara Desert. However, During the Cretaceous period, the Sahara Desert was very green and hospitable. It was abundant in rivers, lakes, low-lying vegetation, and a variety of plants.
The Sahara Desert in the Cretaceous period was a good region for supporting different dinosaur species. Fossil evidence suggests that Nigersaurus shared their habitats with other dinosaurian herbivores, i.e. Apatosaurus. They also had predators that lived in the same region and one of their predators was theropoda.
Behavior and Lifestyle
Nigersaurus is believed to behave much like other herbivore sauropods. They had probably spent most of their time in hang-dog positions and grazing low-lying vegetation. Nigersaurus had difficulty in holding their head upward or horizontally. So eating leaves and other parts of long trees was not possible for them.
Paleontologists believe that their behavior can be compared with today’s cows. Nigersaurus were social and remained herds as a protection strategy. Due to insufficient fossil evidence, the reproduction strategy of Nigersaurus is not known. However, studying the other related sauropods gives a clue that, they would nest in colonies for laying eggs. They also provided food, care, and protection to their offspring.
Diet
Similar to other Sauropods, Nigersaurus were herbivores. They had grazed close to the ground and ate low-lying vegetation. They had a wide muzzle which helped them in cropping more vegetative material in a single bite. You may think they probably ate grass, but the grass hadn’t evolved during that time. The dental structures of Nigersaurus also suggest that they ate soft plants in large amounts to meet their nutritional requirements. They mostly ate angiosperms, horsetails, and ferns as food. Many paleontologists also believe that their 500 closely packed teeth arrangement also functioned like a comb. This comb-like teeth arrangement may have also helped them in filtering and eating aquatic plants.
Discovery
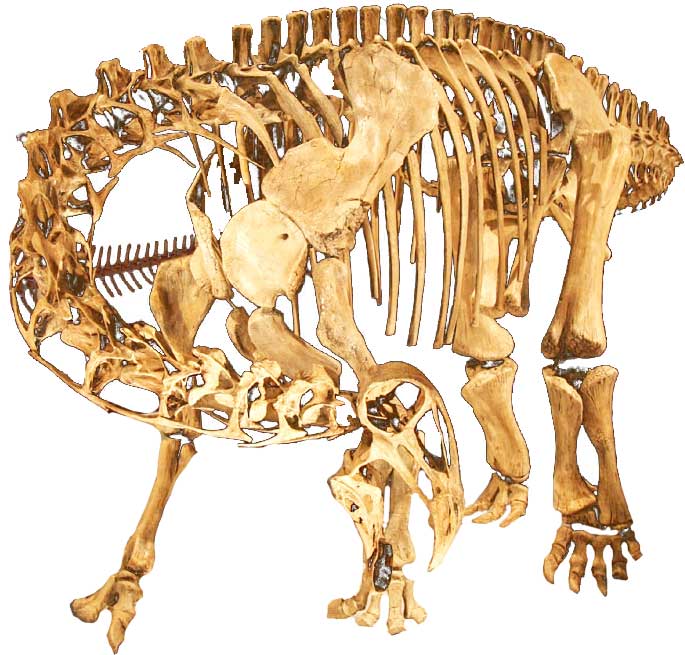 The first remains of Nigersaurus were discovered in 1976. But paleontologists at that time were not sure about their findings. Paul Sereno, an American paleontologist, led expeditions to Niger in the years 1997 and 2000 for the search of fossils. He discovered many fossils from Elrhaz formations in Niger. Among those fossils, he found fossils of a new dinosaur species that is known as Nigersaurus (“Niger Reptile”). He along with other paleontologists gathered many bony parts of Nigersaurus separately and assembled a rough skeleton.
The first remains of Nigersaurus were discovered in 1976. But paleontologists at that time were not sure about their findings. Paul Sereno, an American paleontologist, led expeditions to Niger in the years 1997 and 2000 for the search of fossils. He discovered many fossils from Elrhaz formations in Niger. Among those fossils, he found fossils of a new dinosaur species that is known as Nigersaurus (“Niger Reptile”). He along with other paleontologists gathered many bony parts of Nigersaurus separately and assembled a rough skeleton.
Paul provided a detailed paper on the appearance of Nigersaurus in 2005. He explained its unusual Skull which housed 500 teeth and its feeding adaptions. However, a more detailed paper on the whole Nigersaurus skeleton came in 2007. Currently, many specimens discovered by other paleontologists are under examination and further details will emerge as the research will continue.
For more information goto: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nigersaurus
Facts
- Nigersaurus means Niger-Lizard, but Nigersaurus are not lizards; they are dinosaurs. Dinosaurs and lizards are a distantly related group of reptiles.
- Skull bones of Nigersaurus are very thin, even light could pass through them.
- Nigersaurus are also called Mesozoic cows because their behavior was similar to modern cows.
- Despite elongated nostrils, Nigersaurus’ sense smell was not so good.
- When the first fossils of Nigersaurus were discovered in 1976, paleontologists couldn’t recognize them as a new species. It is because the skeleton fossils were very hollow and distorted.