Voltage
 Voltage is an electrical pressure, which forces the electric charges (electrons) to move in an electrical circuit. Voltage is measured in volts, abbreviated as ‘V’.
Voltage is an electrical pressure, which forces the electric charges (electrons) to move in an electrical circuit. Voltage is measured in volts, abbreviated as ‘V’.
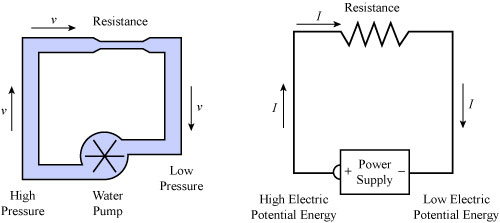
To understand the concept of voltage, consider a water pump which is pumping the water. The pump pushes the water to flow in the pipes. The pump acts like the voltage and the water acts like charges.
However, it is not necessary that when the voltage is applied, the electric charges will flow (current). Charges need a complete closed path to flow.
Current
Electric current is the number of electrons flowing through a point in a circuit. Consider a circuit, which is marked ‘A’ at a point. The number of electrons that will pass through the point ‘A’ in one second will be the current of the circuit. You can consider the current in a circuit as a flow of water in the pipes.
The current in a circuit is caused by the voltage, much like the water flow in the pipes is caused by the pump. Electric current is measured in the amperes, sometimes called “amps”. It is denoted by the letter ‘I’.
Resistance
Resistance, as the name suggests, provides the resistance to the electrical current. It always tries to stop the current from flowing. Every material around the world has resistance for electric current.
Some materials have very small resistance, called conductors. While, other materials have very high resistance, called insulators. We use the conductors in the circuit for electric current to pass easily.
Resistance depends on the structure of the material:
- If a material has more free electrons like metals, it will act as a conductor.
- If a material has fewer free electrons like rubber, it will act as an insulator.
Relationship between Voltage, Current, and Resistance
The relationship between voltage, current, and resistance can be found from the ohm’s law:
V = I*R ; Here, V = Voltage, I = Current, R = Resistance
See the Ohm’s Law for further information.
AC and DC
There are two types of current that flow in a circuit. One is called DC (Direct Current) and other is AC (Alternating Current).
DC – Direct Current
Direct current is the flow of electrons in one direction. Although, the magnitude of the current can decrease or increase but it will always flow in one direction in a circuit. Batteries and charger produce the DC.
AC – Alternating Current
Alternating current doesn’t flow in one direction in a circuit. Instead, it changes its polarity (direction) constantly. The rate of changing polarity is called the frequency of AC. We all use AC current in our homes with 50 to 60 Hertz frequency. AC is often converted into DC by the chargers to charge your laptop and smart phone’s battery.
Interesting Facts
- If the voltage is sufficient enough, electric current can pass through air. Lightning strikes, when the voltage builds enough to pass through air.
- When current pass through a conductor, it produces a magnetic field around it.
- Voltage is measured by a voltmeter. Whereas, current is measured by the ammeter.