 Dating artifacts to determine their age is one of the most important steps in archeology. Determining the accurate age of an object helps archeologists piece together ancient history. Dating is necessary for understanding history timeline and evolution of civilizations over time. For example, the age of pottery and tools artifacts tells us how people lived, how they interacted, and what things they valued most.
Dating artifacts to determine their age is one of the most important steps in archeology. Determining the accurate age of an object helps archeologists piece together ancient history. Dating is necessary for understanding history timeline and evolution of civilizations over time. For example, the age of pottery and tools artifacts tells us how people lived, how they interacted, and what things they valued most.
Without proper dating, it would be impossible to tell whether the artifact was from ancient Rome or dinosaur time. Accurate dating of artifacts helps in figuring out the age of an ancient city and whether it was part of an extraordinary historical event like a catastrophe or a war.
Methods of Dating Artifacts
There are two main ways for determining how old an artifact is; relative dating and absolute dating. These methods help archeologists find the accurate date on which the artifact was made and how it fits with developed history.
Absolute Dating
Absolute dating is the most accurate type of dating that can determine the exact date of artifact creation. The most common method is carbon dating which is used for dating organic substances like bones and wood. The carbon dating method measures the decay of the radioactive isotope of carbon found in organic matter. The other dating method is tree-ring dating in which rings in the trunk of a tree are counted. The rings are formed in the tree trunk over time at a specific rate. The more rings in a tree trunk means it is older.
Relative Dating
Artifacts whose exact date can’t be measured directly can be dated based on the relative dating of objects found in the same area. Various methods help in revealing the relative date of an artifact. For example, studying layers of Soil and the depth at which the artifact is found can determine its age. It is because soil layers grow over time at a specific rate and the time signature is also stored along the way. In general, if an artifact is found deeper, it is older than the artifacts found in upper layers of soil.
Examples of Famous Dated Artifacts
Dating artifacts have uncovered many secrets related to human history and helped us in learning about ancient people. Here are some examples of the most famous artifacts dated by archeologists:
Dead Sea Scrolls
 Dead Sea Scrolls are the oldest manuscripts of the bible found inside the Caves of the Dead Sea. They have been carbon-dated and found to be 2,000 to 2,200 years old. These scrolls reveal the religious practices of people at that time.
Dead Sea Scrolls are the oldest manuscripts of the bible found inside the Caves of the Dead Sea. They have been carbon-dated and found to be 2,000 to 2,200 years old. These scrolls reveal the religious practices of people at that time.
Rosetta Stone
 Since the discovery of pyramids, it was next to impossible to decode and understand the writing of ancient Egyptians. But things changed after the discovery of Rosetta Stone which was dated to be more than 2,200 years old. The stone had the inscription of Egyptian hieroglyphs, demotic, and Greek scripts. We knew the Greek language, which allowed us to translate ancient Egyptian scripts into our modern languages with the help of this stone.
Since the discovery of pyramids, it was next to impossible to decode and understand the writing of ancient Egyptians. But things changed after the discovery of Rosetta Stone which was dated to be more than 2,200 years old. The stone had the inscription of Egyptian hieroglyphs, demotic, and Greek scripts. We knew the Greek language, which allowed us to translate ancient Egyptian scripts into our modern languages with the help of this stone.
Shroud of Turin
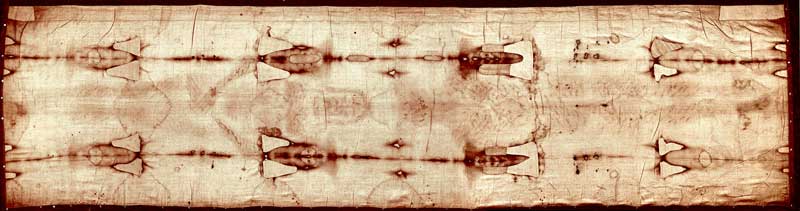 The Shroud of Turin is a piece of cloth that was believed to be wrapped on Jesus’ body after his death. For many centuries no one challenged the true origin of this cloth. When the cloth was Carbon-dated, it was found to be from 13th-century medieval times – much later than the time of Jesus.
The Shroud of Turin is a piece of cloth that was believed to be wrapped on Jesus’ body after his death. For many centuries no one challenged the true origin of this cloth. When the cloth was Carbon-dated, it was found to be from 13th-century medieval times – much later than the time of Jesus.
Why Accurate Dating Matters
Accurately dating artifacts found from the archeological site is a key step in determining their origin. Without proper dating, it would be difficult to piece the history of ancient civilizations together. Also, dating helps archeologists to sort the major events of history in a time sequence. This way it becomes easier to find relations between two ancient civilizations that lived during the same time period.
Fun Facts
- The technique of carbon dating was discovered in 1949 which revolutionized the field of archeology. Before its discovery, archeologists mostly relied on guesses and comparisons with the surrounding environment for estimating the date of an artifact.
- Since ancient times pottery has been hardened on fire. Today scientists use a method called thermoluminescence for measuring the exact date when the pottery was previously fired. In this method, the pottery is heated and then its stored energy is measured.





