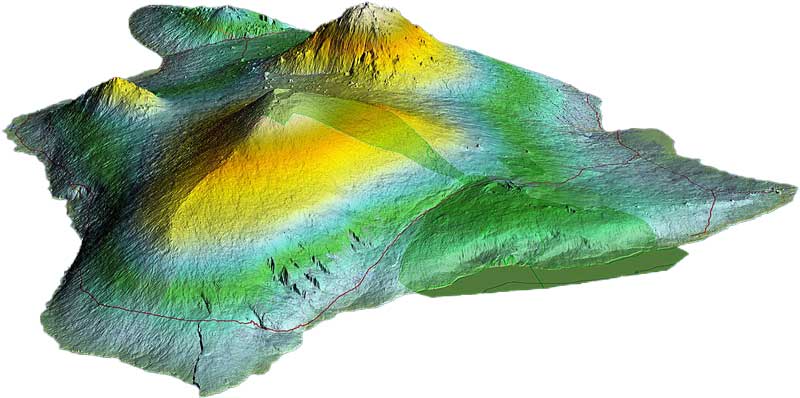
 Topography is an interesting branch of geography in which shapes and features on the surface of the Earth are studied. It helps us understand Mountains, plains, valleys, rivers, and some manmade features, including dams, cities, and roads. It also reveals the complexity and beauty of the Earth’s surface and how different features are connected together.
Topography is an interesting branch of geography in which shapes and features on the surface of the Earth are studied. It helps us understand Mountains, plains, valleys, rivers, and some manmade features, including dams, cities, and roads. It also reveals the complexity and beauty of the Earth’s surface and how different features are connected together.
What Is Topography?
Topography is the careful study of Earth’s surface including natural and man-made features. It covers the shape, size, and arrangements of various landforms and their relationship with each other. The topography of a landform or a region outlines its map when viewed from above and shows details like valleys, hills, buildings, roads, and rivers. Topography is not just limited to Earth, it is also used to study the surface of other planets, moons, and space objects.
The term “topography” is derived from two Greek words “topos” means place, and “graphia” means writing. In simple, topography (topos-graphia) means to draw a physical layout of a place for example, slopes of the Himalayas, flatlands of the Sahara Desert, or turns and twists of any hiking trails.
Types of Topographic Features
Topography covers a large range of features which are mainly grouped into two categories: natural features and man-made features.
Natural Features
Natural features are formed during various geological processes and natural forces over a period of a few hours to millions of years. For example, massive earthquakes can transform the landscape in a matter of a few minutes. Whereas, Erosion by wind happens over millions of years in the mountains. Some of the most common examples are:
- Mountains – Mountains are tall natural structures formed on the Earth’s surface due to the activity of plate tectonics. The peaks of the mountains are usually larger than 300 meters (1,000 feet) from the ground. For example, Mount Everest is the tallest mountain on the Earth reaching a height of 8,849 meters.
- Hills – These are bulges on the Earth’s surface that are smaller than the mountains having a gentle slope to the surrounding landscape.
- Valleys – Valleys are the low-lying areas in between mountains or hills. These are formed rivers over time when they pass between mountains or hills.
- Plains – These are the vast and flat areas on the Earth that are often used for farming purposes due to their rich soil for plant growth.
- Rivers – Rivers are the water bodies that start from the mountains and throughout their way to oceans. They are the major sources of fresh water for wildlife and farming.
- Lakes – These are water bodies that are surrounded by land and remain standstill. They are mostly filled by rivers and rainwater.
Man-Made Features
Humans also alter the Earth’s surface and create new land features, such as:
- Roads and Highways – They connect our cities and towns for easier transportation.
- Buildings and Bridges – They are mostly populated in urban landscapes.
- Canals and Dams – They are made for managing and transporting water efficiently for power generation, transportation, and agriculture.
How Do We Represent Topography?
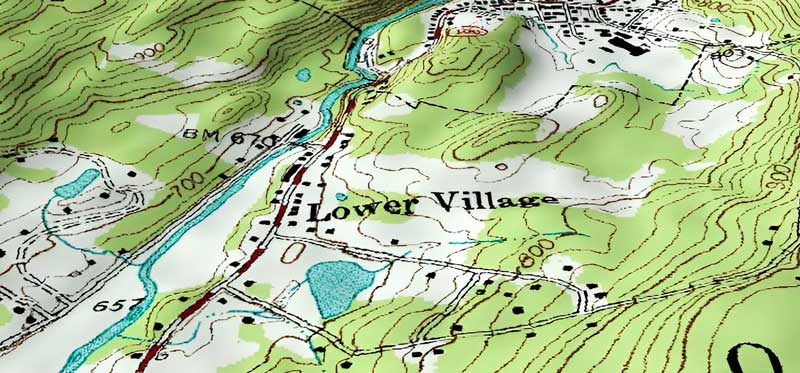 To understand the topography of the landscape, topographic maps are the most common and useful tools. These maps provide a detailed view of the landscape for natural and man-made features.
To understand the topography of the landscape, topographic maps are the most common and useful tools. These maps provide a detailed view of the landscape for natural and man-made features.
Topographic Maps
These are special maps that show the elevation and shape of the land using contour lines, symbols, and colors.
- Contour Lines – These are lines on a map that connects points of equal elevation. When contour lines are too close to each other, they represent hills or mountains. Wider and far away contour lines gentle slopes and plains.
- Symbols and colors – Different symbols are used for marking roads, buildings, forests, cliffs, and water bodies. Moreover, blue colors are used for water bodies and green is mostly used for forests.
Why Is Topography Important?
Studying Earth’s surface using topography plays an important role in shaping our environment and the way we interact with the world. We need topographic maps for urban planning, navigation, water flow, erosion control, and agriculture. Furthermore, understanding the topography of a region helps in predicting and managing natural disasters like landslides, floods, and earthquakes.
Tools for Studying Topography
 Topographic study requires traditional and modern technology to effectively understand the Earth’s surface. But, nowadays we rely mostly on modern technology for creating high-quality topographic maps. We use satellites and drones to capture high-quality images and close-up views of the region. These tools have allowed us to analyze the topography with incredible speed and accuracy.
Topographic study requires traditional and modern technology to effectively understand the Earth’s surface. But, nowadays we rely mostly on modern technology for creating high-quality topographic maps. We use satellites and drones to capture high-quality images and close-up views of the region. These tools have allowed us to analyze the topography with incredible speed and accuracy.
Fun Facts
- Mauna Kea will be the tallest mountain on the Earth if you measure it from its underwater base. This mountain is more than 50% underwater and its height from base to peak is 10 kilometers.
- The flattest region on the Earth is Salar de Uyuni located in Bolivia. It is so flat that sometimes satellite equipment is calibrated here.