 Biomes are the large and unique ecosystems that cover our Earth, with their unique climate, animals, and plants. Biomes shape the world around us, so studying them helps us understand the diversity of life and its delicate balance. Every biome, from deserts to deep Oceans, is a habitat for species that have adapted to their specific environments.
Biomes are the large and unique ecosystems that cover our Earth, with their unique climate, animals, and plants. Biomes shape the world around us, so studying them helps us understand the diversity of life and its delicate balance. Every biome, from deserts to deep Oceans, is a habitat for species that have adapted to their specific environments.
What Are Biomes?
A biome is a vast geographic region with similar animals, plants, and climate conditions. Biomes are classified according to their two main factors: temperature and precipitation. These two factors decide what types of animals will be able to survive in this particular biome. For example, camels and cacti are well adapted to high temperatures and low precipitation environments, making them better suited for the desert biome.
Biomes cover vast geographic regions that can include multiple countries. Unlike an ecosystem, which covers smaller regions and is a part of a biome. For example, the tropical rainforest biome near the equator covers South America, Africa, and Southeast Asian countries.
Types of Biomes on Earth
Biomes are divided into terrestrial and aquatic categories on a broader scale. These categories are further broken into smaller categories for their specific conditions.
Terrestrial Biomes
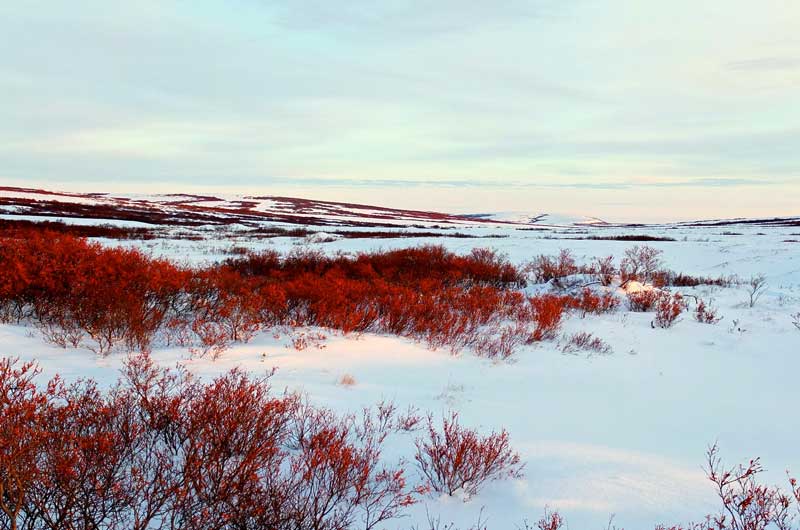

Terrestrial biomes are land-based biomes that are broken down into the following types:
- Tropical Rainforests – They are characterized by dense tree populations having warm and wet climates. They are located near the equator and receive higher precipitation than any other biome.
- Temperate Deciduous Forest – These biomes are located in mid-latitude areas between polar and tropic regions. They have four seasons and are exposed to both warm and cold air masses.
- Deserts – These biomes receive the least precipitation and can have hot temperatures like the Sahara Desert, or cold temperatures in winter like the Gobi Desert. The plants and animals that live here are well adapted to survive in extremely dry and fluctuating temperature conditions.
- Grasslands – They receive moderate rainfall and are covered with grass and fewer trees in their vast open lands. Grasslands can be found in tropical and cold climate regions.
- Tundra – This biome is mostly covered with ice and snow. It has a lower number of animals and plant species due to harsh conditions.
Aquatic Biomes
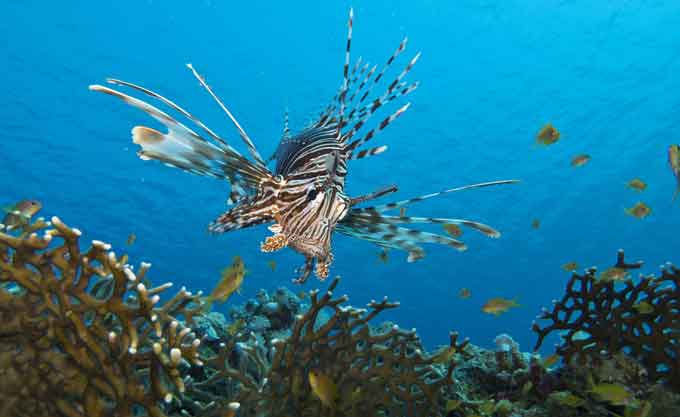 Aquatic biomes are water-based biomes having the following types:
Aquatic biomes are water-based biomes having the following types:
- Freshwater – The freshwater biome is based on freshwater bodies like rivers, lakes, and wetlands. This type of biome supports animals and plants that survive in freshwater environments.
- Marine – The Marine biome includes oceans, coral reefs, and estuaries. It contains the largest life diversity on Earth from tiny planktons to gigantic whales.
Climate and Biomes
Climate plays a key role in shaping any type of biome determined by Temperature and amount of precipitation. Different combinations of temperature and precipitations create unique climates for different biomes that influence the survival of plants and animals.
- Temperature – It directly affects the survival of plants and animals. For instance, the tundra biome which has the coldest climate around the year limits plant growth to small like mosses. On the other hand, tropical rainforests have consistent warm temperatures which supports large and diverse species of plants and animals.
- Precipitation – The amount of precipitation decides how much wet a region could get. For example, deserts receive the least precipitation so they only support drought-resistant plants and animals. On the other hand, rainforests receive a high amount of precipitation so they can support plants and animals which require constant water.
Importance of Biomes
Biomes play a crucial role in maintaining life on the Earth including regulation of natural processes and providing resources to wildlife and humans. They also keep the life forms diversified throughout the planet and provide them habitat to ensure their survival. Without biomes, it is not possible to maintain balance and healthy ecosystems due to environmental changes.
Biomes also play a crucial role in regulating climate. For instance, forests absorb massive amounts of carbon dioxide and in turn, release oxygen gas to reduce climate change. Oceans also help regulate global temperature and the water cycle. The protection of biomes is very critical for ensuring the survival of all living beings on the Earth.
Fun Facts
- Rainforests are also known as medicine factories because 25% of modern medicines are derived from plants that inhabit rainforests.
- The marine biome is the largest biome on the Earth that covers 70% of the Earth’s surface.