The universe is a sort of thing in which everything, which we know of, lives including humans, Earth, planets, stars, black holes, and galaxies etc. Our universe is full of mysteries and unexplained events that amaze scientists around the world regularly.
What is the Universe?
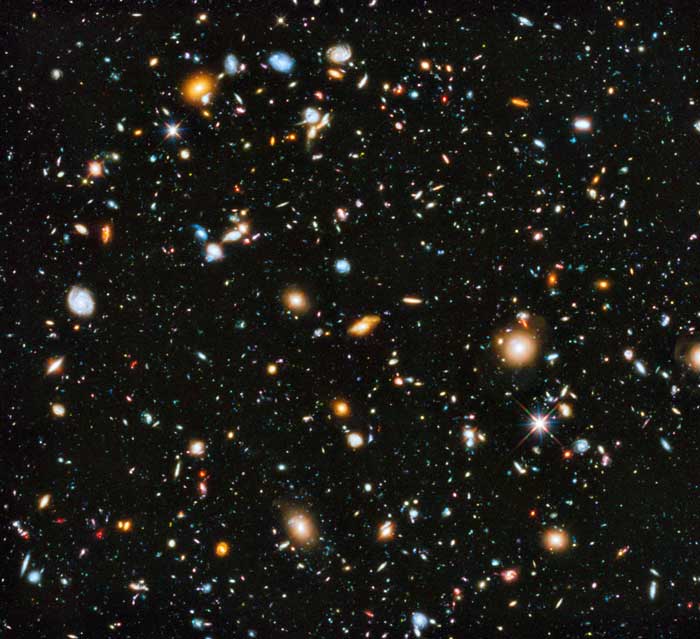

The definition of the universe is still incomplete because there are many observations that are still unexplained. But, in short, you can consider the universe as a thing that has space, time, and other stuff.
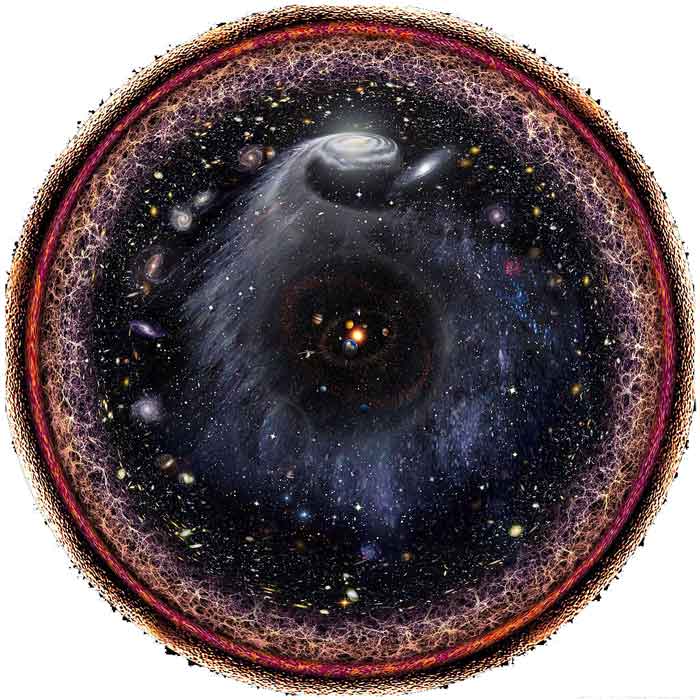
The actual size of our universe is not known because there are certain physical phenomena, such as the speed of light, that are restricting us from observing the whole universe. The universe that scientists can observe with science instruments is called “observable universe”. The current diameter of the observable universe is found to be around 93 billion light-years (1 light year = 9461 billion kilometers).
What is inside the Universe?
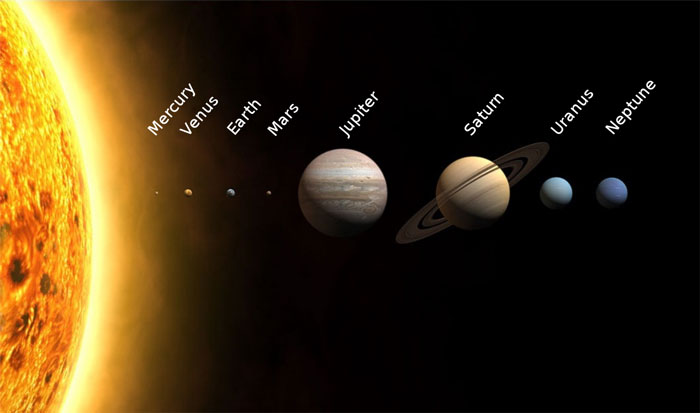
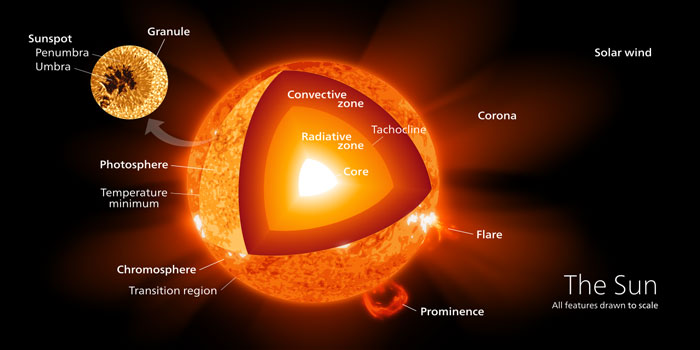
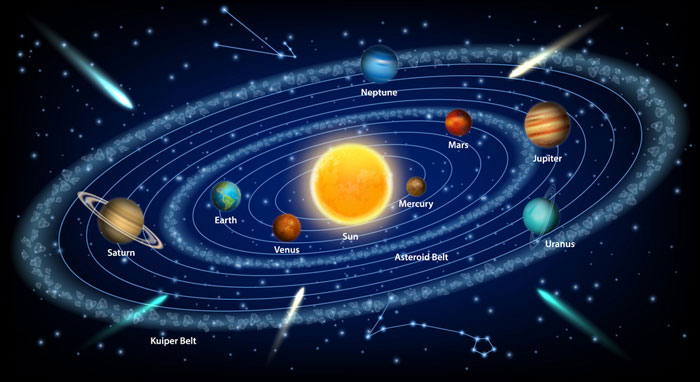
Our universe contains many types of objects and mysterious things. Some of these things you may know very well, such as planets, moons, asteroids, comets, stars, galaxies, and black holes, etc. All of these objects are made of matter. There are also many mysterious things that, we know indirectly, are the part of the universe, such as dark matter and dark energy.
Birth of the Universe – The Big Bang Theory
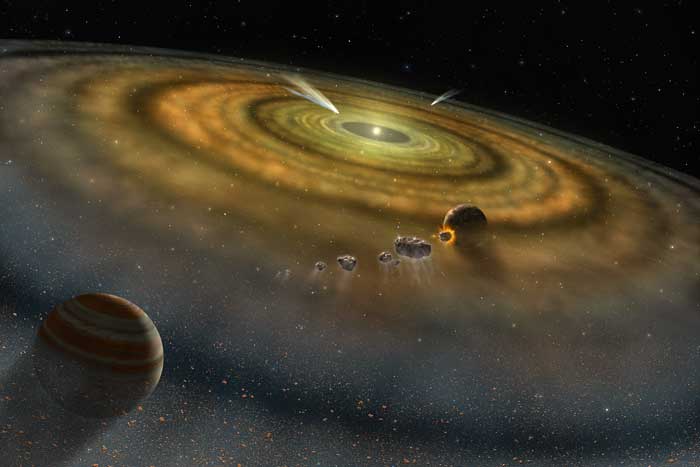
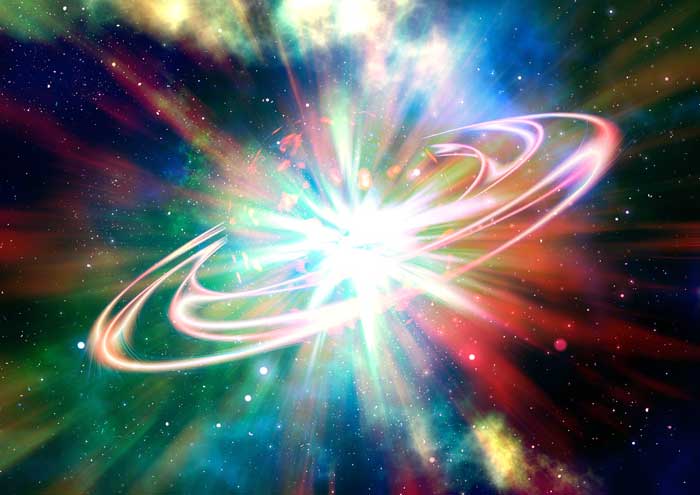 Scientists have estimated that our universe was formed around 14 billion years ago. The formation of our universe is described by the theory of the big bang. The theory describes that our universe started its journey from the rapid expansion of something that was very small, dense, and hot. After the rapid expansion, the universe continued to expand and the formation of cosmic objects began until now.
Scientists have estimated that our universe was formed around 14 billion years ago. The formation of our universe is described by the theory of the big bang. The theory describes that our universe started its journey from the rapid expansion of something that was very small, dense, and hot. After the rapid expansion, the universe continued to expand and the formation of cosmic objects began until now.
One of the strange and interesting facts is that our universe is still expanding today at an accelerating rate. Scientists have explained the accelerated expansion by the presence of mysterious energy called dark energy. After the rapid expansion, it took around 380,000 years for the first atoms to be formed – that were the atoms of hydrogen. The first stars that illuminated the sky started to appear 200 million years after the rapid expansion of the universe.
Dark Matter and Dark Energy
Dark matter and dark energy are one of the least known things in our universe. Scientists don’t have direct evidence for their existence, they only know them indirectly. For example, the existence of dark matter was found from the gravitational force which they exert on our normal matter. The reason we don’t know much about dark matter is that dark matter doesn’t interact with electromagnetic forces. In other words, it doesn’t interact with light and can pass through normal matter without being noticed.
Dark energy, on the other hand, was found from the fact that our universe is still expanding at an accelerating rate. The unknown source of energy that is powering the accelerating expansion of the universe is dark energy. The word ‘dark’ can be a bit confusing, but it is used because we don’t know much about these things.
Facts
- We get the clue of the expansion of the universe from the fact that galaxies are going away from each other with each passing moment.
- Our universe has no center because all the galaxies are uniformly distributed in the observable universe.
- The multiverse is a concept that is used to describe more than one universes.