Black holes are one of the most interesting objects while studying astronomy. They were once considered as objects of science fiction. But today, they are a reality and one of the mysterious objects in the universe.
Black holes are one of the most interesting objects while studying astronomy. They were once considered as objects of science fiction. But today, they are a reality and one of the mysterious objects in the universe.
What is a Black Hole?
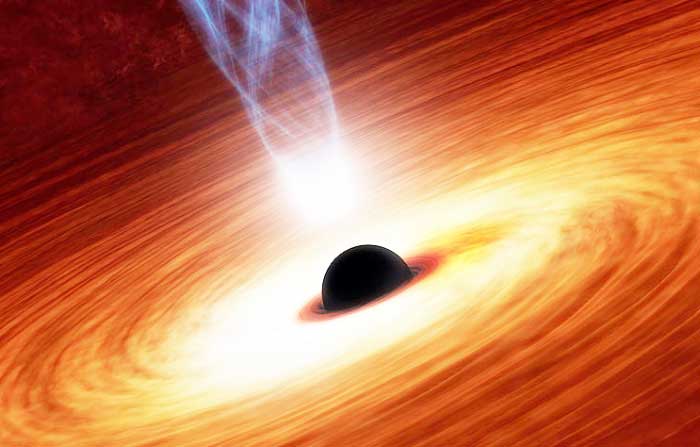
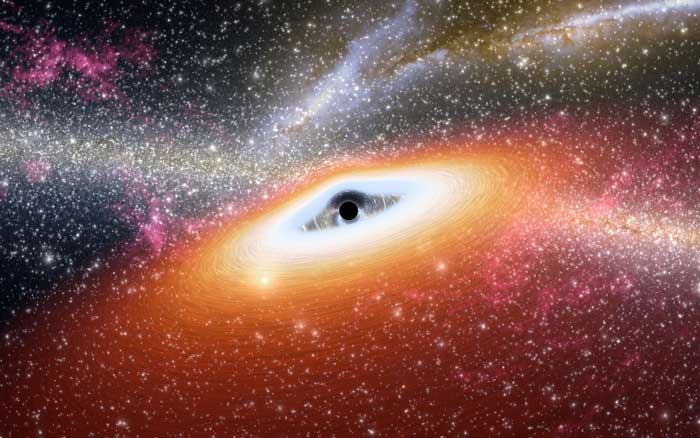 Black holes are objects in our universe that are known for their very strong gravity. The gravity of a black is so strong that no object (e.g. stars) or light can escape from it. They are very massive objects that have a mass of 10 times to a few billion times the mass of our Sun.
Black holes are objects in our universe that are known for their very strong gravity. The gravity of a black is so strong that no object (e.g. stars) or light can escape from it. They are very massive objects that have a mass of 10 times to a few billion times the mass of our Sun.
The thing that makes black holes to have a very strong gravity is its compactness. All the matter in a black hole is compressed so much that it only occupies a very small point in space, also called the singularity.
Formation of Black Holes
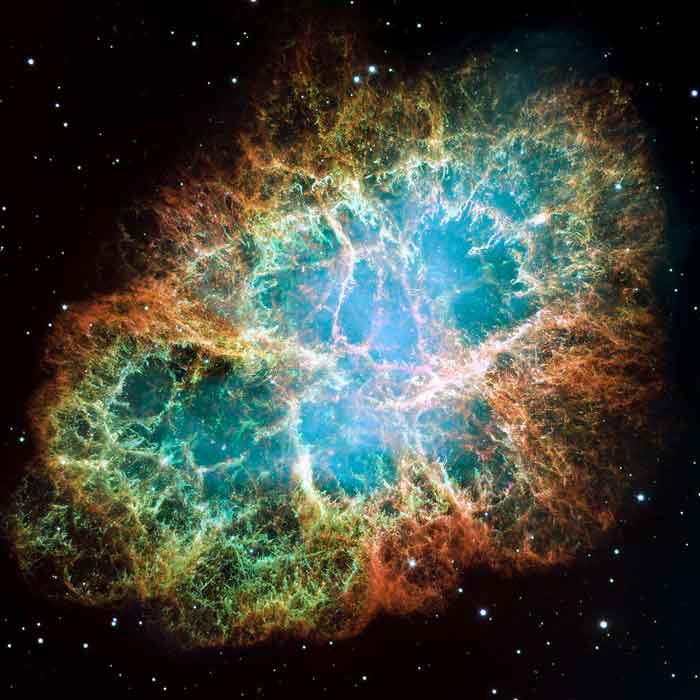

There are several ways in which black holes are formed. But most of the black holes are formed when a large star dies. When a large star consumes all of its nuclear fuel, it starts to collapse. Then suddenly it bursts into the universe’s most powerful explosion, called a supernova.
After the supernova, the remaining core of the star undergoes a sudden collapse due to its own gravity. The matter is compressed so much that its density reaches to infinity at the center, and a black is formed. Due to infinite density, the gravity at the center of black becomes infinite and is called a singularity. You can consider singularity as a single point with infinite density and gravity where the laws of physics, as we know them, breaks.
Properties of a Black Hole
Black holes can’t be seen directly with naked eyes or telescopes, because light can’t escape its immense gravity. Scientists find black holes by observing light and objects that surround it. Black holes are perfect spheres and are featureless objects. But they may have a charge which is found when a black hole repels like-charges and attracts opposite charges.
Event Horizon
 Black holes are dark and they can have various sizes, e.g. some are the size of a city while larger ones can reach half the size of our solar system. The size of a black hole is actually the size of its event horizon. An event horizon is the defining boundary of a black beyond which nothing comes out of a black hole. Moreover, beyond the event horizon, our laws of physics break and scientists are still unaware what could be inside an event horizon?
Black holes are dark and they can have various sizes, e.g. some are the size of a city while larger ones can reach half the size of our solar system. The size of a black hole is actually the size of its event horizon. An event horizon is the defining boundary of a black beyond which nothing comes out of a black hole. Moreover, beyond the event horizon, our laws of physics break and scientists are still unaware what could be inside an event horizon?
Facts
- The largest black hole in our universe has a mass of 66 billion times the mass of our Sun.
- Stephen Hawking has found that black holes also emit certain radiation called Hawking radiation. Due to this fact, black holes have a limited lifespan and they also evaporate.
- Supermassive black holes have the mass of several billion times the mass of our Sun. It is considered that supermassive black holes are present at the center of galaxies.