 James Watt holds high standing in science. Being an inventor, he loved working on machines. Since the steam engine was already introduced, he improved it very nicely to make it useful in society. With his finest skills in making instruments, he made several inventions. This trade made him a rich person. His contributions earned him around five patents in the field of science. Horse Power and the S.I unit of power, Watt, are his additions in science.
James Watt holds high standing in science. Being an inventor, he loved working on machines. Since the steam engine was already introduced, he improved it very nicely to make it useful in society. With his finest skills in making instruments, he made several inventions. This trade made him a rich person. His contributions earned him around five patents in the field of science. Horse Power and the S.I unit of power, Watt, are his additions in science.
Biography – Lifespan
He was born on 19th January 1736 at Greenock, Renfrewshire, Scotland in the house of a ship-builder. James Watt received his early education at home. Later, He was admitted to Greenock Grammar School for further studies. There he became interested in mathematics, leaving Greek and Latin.
After school, he worked with his father and learned to make instruments. But the trade couldn’t last for long. Therefore, he moved to Glasgow to earn money for living. When he turned 18 years old, his mother passed away. He went to London to have training on instruments making and got back to Glasgow after a year.
At Glasgow, he was out of money. By this time, he got the chance to repair the astronomical instruments of Alexander Macfarlane – a Scottish mathematician. The instruments that he repaired were kept in Macfarlane Observatory at the University of Glasgow. His work was liked by the university management and was offered to work there. He set up a laboratory and worked ahead. It was this laboratory where he invented instruments like the quadrant, the barometer, and parts of the telescope. The quadrant is an instrument used for measuring angle up to 90 degrees. Whereas, a barometer is a scientific instrument that is used for measuring air pressure.
James Watt’s important part of life was work on the Newcomen’s steam engine. He is said to have got the idea of using steam from a kettle that boiled the water and whose pressurized steam pushed-up the cap. He succeeded in his work of improving the steam engine and got a patent on his name. He later made a partner, Mathew Bolton, who invested in his work. They built a work-place called Soho Factory, where machines were designed and built. James spent his last days in Birmingham, England and died there on 25th August 1819.
Contributions and Discoveries
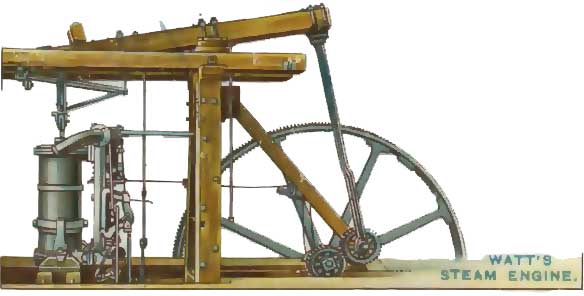
Hard work paid to James Watt in his life. His achievements are reflected in the patents which he earned based on his works. The man behind the Industrial Revolution is none other than James Watt. His contributions in science laid the ground-work for engineers to use energy properly and save it from getting wasted.
Here are some of his main inventions and contributions:
- Improved Steam Engine – James watt added new parts like condenser to press the steam. This improved the efficiency of the engine.
- Governor Mechanism – Before the inventions of governor mechanism the steam engines used in industries have to be manually adjusted according to load. James Watt invented the governor mechanism which automatically adjusted throttle to adjust according to load.
- Patents – He got patents for reducing steam waste, circular motion in the steam engine, and making furnace – a hot place where heat is generated. For your information, the patent is a legal right to prevent others from making or selling the products without permission from the patent holder.
- Horse Power – He gave the concept of horse-power. That means load lifted by horse in one second. He derived that 745 HP is a basic unit of mechanical power.
- Production of Chlorine – He helped his Father-in-Law McGregor – a British chemist – to chemically produce Chlorine.
Interesting Facts
- Due to his ability of deriving units, the basic unit for measuring power was named Watt by International System of Units or S.I units in 1960.
- James Watt became a fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburg in 1784 for his valuable works in science.





